Note
Click here to download the full example code
Benchmark inference for a linear regression#
This short code compares the execution of a couple of runtime for inference including onnxruntime. This benchmark leverages the example Benchmark Linear Regression. This simple model is useful to measure unsignificant cost for large models.
Linear Regression#
import warnings
from time import perf_counter as time
from multiprocessing import cpu_count
import numpy
from numpy.random import rand
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas
from onnxruntime import InferenceSession
from onnxruntime.capi._pybind_state import ( # pylint: disable=E0611
SessionIOBinding, OrtDevice as C_OrtDevice)
from sklearn import config_context
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.utils._testing import ignore_warnings
from skl2onnx import to_onnx
from skl2onnx.common.data_types import FloatTensorType
from mlprodict.onnxrt import OnnxInference
Available optimisation on this machine.
from mlprodict.testing.experimental_c_impl.experimental_c import code_optimisation
print(code_optimisation())
AVX-omp=8
Implementations to benchmark#
def fcts_model(X, y, n_jobs):
"LinearRegression."
model = LinearRegression(n_jobs=n_jobs)
model.fit(X, y)
initial_types = [('X', FloatTensorType([None, X.shape[1]]))]
onx = to_onnx(model, initial_types=initial_types,
black_op={'LinearRegressor'})
sess = InferenceSession(onx.SerializeToString(),
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])
outputs = [o.name for o in sess.get_outputs()]
oinf = OnnxInference(onx, runtime="python")
bind = SessionIOBinding(sess._sess)
# ort_device = C_OrtDevice.cpu()
ort_device = C_OrtDevice(
C_OrtDevice.cpu(), C_OrtDevice.default_memory(), 0)
def predict_skl_predict(X, model=model):
return model.predict(X)
def predict_onnxrt_predict(X, sess=sess):
return sess.run(outputs[:1], {'X': X})[0]
def predict_onnx_inference(X, oinf=oinf):
return oinf.run({'X': X})["variable"]
def predict_onnxrt_predict_bind(X, sess=sess, bind=bind,
ort_device=ort_device):
if X.__array_interface__['strides'] is not None:
raise RuntimeError("onnxruntime only supports contiguous arrays.")
bind.bind_input('X', ort_device, X.dtype, X.shape,
X.__array_interface__['data'][0])
bind.bind_output('variable', ort_device)
sess._sess.run_with_iobinding(bind, None)
ortvalues = bind.get_outputs()
return ortvalues[0].numpy()
return {'predict': {
'skl': predict_skl_predict,
'ort': predict_onnxrt_predict,
'numpy': predict_onnx_inference,
'ort-bind': predict_onnxrt_predict_bind
}}
Benchmarks#
def allow_configuration(**kwargs):
return True
def bench(n_obs, n_features, n_jobss,
methods, repeat=10, verbose=False):
res = []
for nfeat in n_features:
ntrain = 50000
X_train = numpy.empty((ntrain, nfeat)).astype(numpy.float32)
X_train[:, :] = rand(ntrain, nfeat)[:, :]
eps = rand(ntrain) - 0.5
y_train = X_train.sum(axis=1) + eps
for n_jobs in n_jobss:
fcts = fcts_model(X_train, y_train, n_jobs)
for n in n_obs:
for method in methods:
if not allow_configuration(n=n, nfeat=nfeat,
n_jobs=n_jobs, method=method):
continue
obs = dict(n_obs=n, nfeat=nfeat, method=method,
n_jobs=n_jobs)
# creates different inputs to avoid caching in any ways
Xs = []
for r in range(repeat):
x = numpy.empty((n, nfeat))
x[:, :] = rand(n, nfeat)[:, :]
Xs.append(x.astype(numpy.float32))
for name, fct in fcts[method].items():
if name == 'skl':
# measures the baseline
with config_context(assume_finite=True):
st = time()
repeated = 0
for X in Xs:
p1 = fct(X)
repeated += 1
if time() - st >= 1:
break # stops if longer than a second
end = time()
obs["time_skl"] = (end - st) / repeated
else:
st = time()
r2 = 0
for X in Xs:
p2 = fct(X)
r2 += 1
if r2 >= repeated:
break
end = time()
obs["time_" + name] = (end - st) / r2
# final
res.append(obs)
if verbose and (len(res) % 1 == 0 or n >= 10000):
print("bench", len(res), ":", obs)
# checks that both produce the same outputs
if n <= 10000:
if len(p1.shape) == 1 and len(p2.shape) == 2:
p2 = p2.ravel()
try:
assert_almost_equal(
p1.ravel(), p2.ravel(), decimal=5)
except AssertionError as e:
warnings.warn(str(e))
return res
Graphs#
def plot_rf_models(dfr):
def autolabel(ax, rects):
for rect in rects:
height = rect.get_height()
ax.annotate(f'{height:1.1f}x',
xy=(rect.get_x() + rect.get_width() / 2, height),
xytext=(0, 3), # 3 points vertical offset
textcoords="offset points",
ha='center', va='bottom',
fontsize=8)
engines = [_.split('_')[-1] for _ in dfr.columns if _.startswith("time_")]
engines = [_ for _ in engines if _ != 'skl']
for engine in engines:
dfr[f"speedup_{engine}"] = dfr["time_skl"] / dfr[f"time_{engine}"]
print(dfr.tail().T)
ncols = 2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(len(engines), ncols, figsize=(
14, 4 * len(engines)), sharey=True)
row = 0
for row, engine in enumerate(engines):
pos = 0
name = f"LinearRegression - {engine}"
for nf in sorted(set(dfr.nfeat)):
for n_jobs in sorted(set(dfr.n_jobs)):
sub = dfr[(dfr.nfeat == nf) & (dfr.n_jobs == n_jobs)]
ax = axs[row, pos]
labels = sub.n_obs
means = sub[f"speedup_{engine}"]
x = numpy.arange(len(labels))
width = 0.90
rects1 = ax.bar(x, means, width, label='Speedup')
if pos == 0:
# ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_ylim([0.1, max(dfr[f"speedup_{engine}"])])
if pos == 0:
ax.set_ylabel('Speedup')
ax.set_title('%s\n%d features\n%d jobs' % (name, nf, n_jobs))
if row == len(engines) - 1:
ax.set_xlabel('batch size')
ax.set_xticks(x)
ax.set_xticklabels(labels)
autolabel(ax, rects1)
for tick in ax.xaxis.get_major_ticks():
tick.label.set_fontsize(8)
for tick in ax.yaxis.get_major_ticks():
tick.label.set_fontsize(8)
pos += 1
fig.tight_layout()
return fig, ax
Run benchs#
@ignore_warnings(category=FutureWarning)
def run_bench(repeat=200, verbose=False):
n_obs = [1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000]
methods = ['predict']
n_features = [10, 50]
n_jobss = [cpu_count()]
start = time()
results = bench(n_obs, n_features, n_jobss,
methods, repeat=repeat, verbose=verbose)
end = time()
results_df = pandas.DataFrame(results)
print("Total time = %0.3f sec cpu=%d\n" % (end - start, cpu_count()))
# plot the results
return results_df
name = "plot_linear_regression"
df = run_bench(verbose=True)
# df.to_csv("%s.csv" % name, index=False)
# df.to_excel("%s.xlsx" % name, index=False)
somewhere/workspace/onnxcustom/onnxcustom_UT_39_std/_doc/examples/plot_benchmark_inference.py:110: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in cast
X_train = numpy.empty((ntrain, nfeat)).astype(numpy.float32)
bench 1 : {'n_obs': 1, 'nfeat': 10, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00014727494039107114, 'time_ort': 4.714031470939517e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.00017335977521724998, 'time_ort-bind': 8.465053513646126e-05}
bench 2 : {'n_obs': 10, 'nfeat': 10, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00014802228484768422, 'time_ort': 4.3403309537097815e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.0001723297848366201, 'time_ort-bind': 8.037597523070872e-05}
bench 3 : {'n_obs': 100, 'nfeat': 10, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00014994021505117415, 'time_ort': 4.842480004299432e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.0001739592698868364, 'time_ort-bind': 8.561287017073482e-05}
bench 4 : {'n_obs': 1000, 'nfeat': 10, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00016795482486486435, 'time_ort': 0.00010173700517043471, 'time_numpy': 0.0001904038997599855, 'time_ort-bind': 0.0001394052745308727}
bench 5 : {'n_obs': 10000, 'nfeat': 10, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00024241416540462523, 'time_ort': 0.0005774804297834635, 'time_numpy': 0.0004475092148641124, 'time_ort-bind': 0.0006537431053584441}
somewhere/workspace/onnxcustom/onnxcustom_UT_39_std/_doc/examples/plot_benchmark_inference.py:110: RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in cast
X_train = numpy.empty((ntrain, nfeat)).astype(numpy.float32)
bench 6 : {'n_obs': 1, 'nfeat': 50, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.0002696786349406466, 'time_ort': 8.701475511770696e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.00017341562488581985, 'time_ort-bind': 8.145981468260288e-05}
bench 7 : {'n_obs': 10, 'nfeat': 50, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00015068760490976273, 'time_ort': 4.558282962534577e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.0001746026100590825, 'time_ort-bind': 8.327689545694738e-05}
bench 8 : {'n_obs': 100, 'nfeat': 50, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00015511580975726246, 'time_ort': 6.745906546711921e-05, 'time_numpy': 0.00017876612022519112, 'time_ort-bind': 0.00010468032502103597}
bench 9 : {'n_obs': 1000, 'nfeat': 50, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00019505485019180924, 'time_ort': 0.00029141116479877385, 'time_numpy': 0.0002046256046742201, 'time_ort-bind': 0.0003304108651354909}
bench 10 : {'n_obs': 10000, 'nfeat': 50, 'method': 'predict', 'n_jobs': 8, 'time_skl': 0.00044694092008285225, 'time_ort': 0.0009776719298679381, 'time_numpy': 0.0008014900353737176, 'time_ort-bind': 0.0009818153851665556}
Total time = 5.836 sec cpu=8
Results#
df
Graph#
fig, ax = plot_rf_models(df)
fig.savefig(f"{name}.png")
# plt.show()
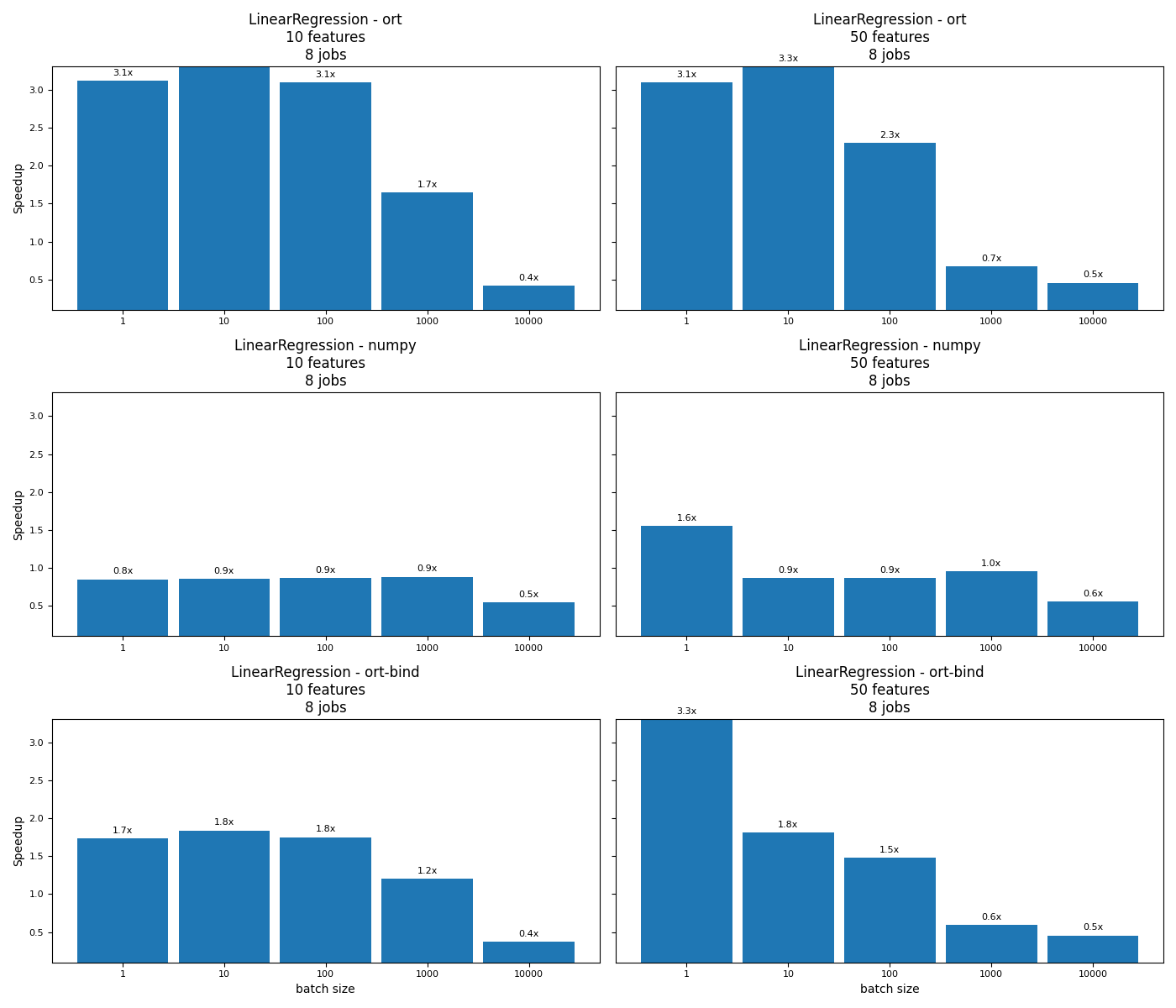
5 6 7 8 9
n_obs 1 10 100 1000 10000
nfeat 50 50 50 50 50
method predict predict predict predict predict
n_jobs 8 8 8 8 8
time_skl 0.00027 0.000151 0.000155 0.000195 0.000447
time_ort 0.000087 0.000046 0.000067 0.000291 0.000978
time_numpy 0.000173 0.000175 0.000179 0.000205 0.000801
time_ort-bind 0.000081 0.000083 0.000105 0.00033 0.000982
speedup_ort 3.099229 3.305798 2.299406 0.669346 0.457148
speedup_numpy 1.5551 0.863032 0.867703 0.953228 0.557638
speedup_ort-bind 3.310573 1.809477 1.481805 0.59034 0.455219
somewhere/workspace/onnxcustom/onnxcustom_UT_39_std/_doc/examples/plot_benchmark_inference.py:232: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The label function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.1 and will be removed in 3.8. Use Tick.label1 instead.
tick.label.set_fontsize(8)
somewhere/workspace/onnxcustom/onnxcustom_UT_39_std/_doc/examples/plot_benchmark_inference.py:234: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The label function was deprecated in Matplotlib 3.1 and will be removed in 3.8. Use Tick.label1 instead.
tick.label.set_fontsize(8)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 8.569 seconds)